Windows 7 Godmode
Windows 7 Godmode
GodMode.{ED7BA470-8E54-465E-825C-99712043E01C}
Uninstall trendMicro client – scripted

| For32-bit OS: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\TrendMicro For 64-bit OS: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6232Node\TrendMicroWorryFree7 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\TrendMicro\UniClient\1600\Misc.] [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6232Node\TrendMicro\UniClient\1600\Misc.] (Probably!) Worry free 7 – Automatic uninstallation script x86/x64 REQUIRES UAC ELEVATION !!!!!! aka do run as admin…. ———————————– regedit /S %temp%\t.reg ———————————- uninstall guiden finner man under ”Wolfie” [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall] |
|||||||
Check .net framework version
.NET Framework
Klipp in detta script i adressfältet på explorer…
javascript:alert(navigator.userAgent)
Snabb koll kan man göra i följande mapp: %systemroot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework
dir %WINDIR% \Microsoft.Net\Framework\v*
.Net Framework History
- .NET Framework 1.0 Beta 1 v1.0.????.0 on Nov 2000
- .NET Framework 1.0 Beta 2 v1.0.2914.0 on Jun 2001
- .NET Framework 1.0 RTM v1.0.3705.0 on Jan 2002
- .NET Framework 1.0 SP1 v1.0.3705.209 on Mar 2002
- .NET Framework 1.0 SP2 v1.0.3705.288 on Aug 2002
- .NET Framework 1.0 SP3 v1.0.3705.6018 on Aug 2004
- .NET Framework 1.1 RTM v1.1.4322.573 on Apr 2003
- .NET Framework 1.1 SP1 v1.1.4322.2032 on Aug 2004
- .NET Framework 1.1 SP1 v1.1.4322.2300 on Mar 2005 (Windows 2003)
- .NET Framework 2.0 RTM v2.0.50727.42 on Nov 2005
- .NET Framework 3.0 RTM v3.0.4506.30 on Nov 2006
- .NET Framework 3.5 Beta 1 v3.5 on Apr 2007
- .NET Framework 3.5 Beta 2 v3.5 on Jul 2007
- .NET Framework 3.5 RTM v3.5on Nov2007
- .NET Framework4.0 Beta 1 v4.0 onMay 2009
- .NET Framework4.0 Beta2 v4.0 onOct 2009
- .NET Framework4.0RC v4.0 onFeb 2010
- .NET Framework4.0RTM v4.0 on????
Versions of the .NET Framework
The released versions of the .NET Framework have the following version information.
| .NET Framework version | Revision | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | Original release | 3.5.21022.8 |
| 3.5 | Service Pack 1 | 3.5.30729.1 |
| 3.0 | Original release | 3.0.4506.30 |
| 3.0 | Service Pack 1 | 3.0.4506.648 |
| 3.0 | Service Pack 2 | 3.0.4506.2152 |
| 2.0 | Original release | 2.0.50727.42 |
| 2.0 | Service Pack 1 | 2.0.50727.1433 |
| 2.0 | Service Pack 2 | 2.0.50727.3053 |
| 1.1 | Original release | 1.1.4322.573 |
| 1.1 | Service Pack 1 | 1.1.4322.2032 |
| 1.1 | Service Pack 1 (Windows Server 2003 32-bit version*) | 1.1.4322.2300 |
| 1.0 | Original release | 1.0.3705.0 |
| 1.0 | Service Pack 1 | 1.0.3705.209 |
| 1.0 | Service Pack 2 | 1.0.3705.288 |
| 1.0 | Service Pack 3 | 1.0.3705.6018 |
Visa och överföra FSMO-roller i Windows Server 2003
FSMO-roller
I en skog finns det minst fem FSMO-roller som tilldelas till en eller flera domänkontrollanter.
De fem FSMO-rollerna är:
Schemahanterare: Domänkontrollanten som är schemahanterare styr alla uppdateringar och ändringar av schemat. För att kunna uppdatera schemat för en skog måste du ha tillgång till schemahanteraren. Det kan bara finnas en schemahanterare i hela skogen.
Domännamngivningshanterare: Domänkontrollanten som är domännamngivningshanterare styr tillägg och borttagning av domäner i skogen. Det kan bara finnas en domännamngivningshanterare i hela skogen.
Infrastrukturhanterare: Infrastrukturhanteraren ansvarar för att uppdatera referenser från objekt i sin domän till objekt i andra domäner. Vid ett givet tillfälle kan det bara finnas en domänkontrollant som fungerar som infrastrukturhanterare i varje enskild domän.
RID-hanterare (Relative ID): RID-hanteraren ansvarar för bearbetning av RID-poolsförfrågningar från alla domänkontrollanter i en viss domän. Vid ett givet tillfälle kan det bara finnas en domänkontrollant som fungerar som RID-hanterare i domänen.
PDC-emulator: PDC-emulatorn är en domänkontrollant som annonserar sig själv som primär domänkontrollant (PDC) till arbetsstationer, medlemsservrar och domänkontrollanter med tidigare versioner av Windows. Om domänen till exempel innehåll
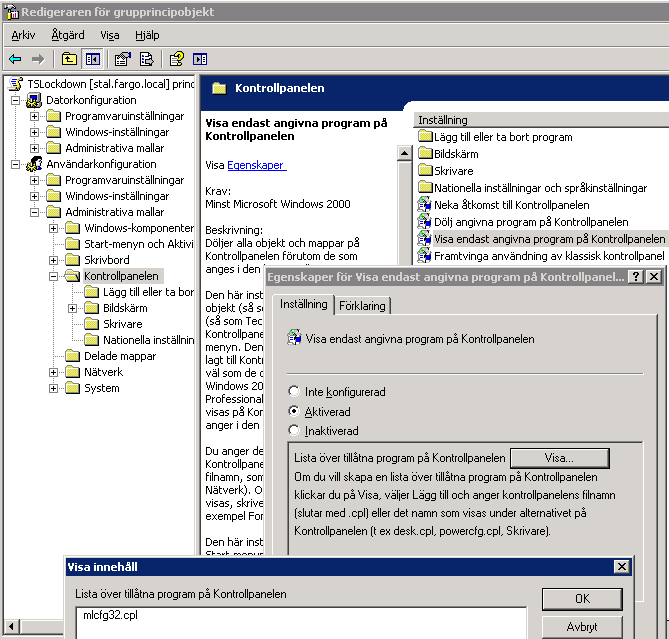
GP 2003 Controlpanel only…
HOWTO: Update Linksys PAP2 Firmware
PAP2 Firmware Update
Easiest way to do this is via the ”upgrade URL,” the syntax for which is https://IPofPAP2/admin/upgrade?protocol://IPofServer/pathto.bin where [protocol] is http or tftp.
So, pasting ”https://192.168.2.20/admin/upgrade?https://192.168.2.10/spa.bin” into your browser would tell the PAP2 at 192.168.2.20 to download and install the firmware bin file located at https://192.168.2.10/spa.bin.
Please note binx is evidently NOT supported name syntax…. just rename it to bin…
Vista/Win7 Virtual Store
File System and Registry Virtualization
As mentioned previously, many legacy Windows applications were created so you could access parts of the file system and registry that are now locked in Windows Vista, and many of these applications are not being immediately updated. However, Microsoft has devised an interesting solution within Windows Vista to provide backward compatibility so that legacy software still works.
If legacy applications attempt to access protected portions of the file system and registry without the proper permissions, UAC virtualization services silently redirect read and write operations from protected portions of the file system and registry to unprotected user-specific locations. This process is transparent to legacy software and occurs automatically.
Virtualization Example
For example, take a legacy software application that attempts to write to a configuration INI file located in:
C:\Program Files\<application>\Setup.ini
Windows Vista automatically detects that you do not have permission to save to that location. Windows Vista then copies the file (if it already exists) to:
C:\Users\<your_account>\AppData\Local\VirtualStore\Program Files\<application>\Setup.ini
Windows Vista then allows the write operation to succeed at the new file in the VirtualStore folder. Subsequent read and write operations for that file will always use the file copy located in the VirtualStore folder. However, the application will continue to believe that it is accessing the Program Files directory
For most cases this solution is sufficient, but it is not perfect. Data that the application thinks is globally accessible now becomes private to the user and almost invisible to other applications unless they also have virtualization enabled (typically only other legacy applications). Some applications will see one file, and some the other. If the application later tries to delete the INI file, the delete will appear to succeed, yet the file will still exist in the Program Files directory and remain visible to the application. If it retries the delete, an access denied exception will be thrown.
Although the majority of legacy applications run with virtualization, it is a short-term measure, not a long-term solution. Microsoft has already warned that you should not depend on virtualization being a part of future Windows releases after Windows Vista.
Various issues may occur on a Windows Server 2003-based computer that is running the Volume Shadow Copy Service
VSS får ibland ”spattet” och behöver omregistreras…
Lösning:
To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
- Click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- Type the following commands at a command prompt. Press ENTER after you type each command.
- cd /d %windir%\system32
- Net stop vss
- Net stop swprv
- regsvr32 ole32.dll
- regsvr32 oleaut32.dll
- regsvr32 vss_ps.dll
- vssvc /register
- regsvr32 /i swprv.dll
- regsvr32 /i eventcls.dll
- regsvr32 es.dll
- regsvr32 stdprov.dll
- regsvr32 vssui.dll
- regsvr32 msxml.dll
- regsvr32 msxml3.dll
- regsvr32 msxml4.dll
Note The last command may not run successfully.
Secure TS 2003
Use Active Directory Users and Computers to create a new organizational unit (OU). Right-click the OU, click Properties, and then on the Group Policy tab, click New Policy. Edit this policy with the following settings:
[Computer Configuration\Admin Templates\System\Group Policy]
Enable the following setting:
User Group Policy loopback processing mode
[Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options]
Enable the following settings:
Do not display last user name in logon screen
Restrict CD-ROM access to locally logged-on user only
Restrict floppy access to locally logged-on user only
[Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Installer]
Enable the following setting, and set it to Always:
Disable Windows Installer
Note The default setting for Disable Windows Installer prevents any non-managed applications from being installed by a non-administrator. Setting Disable Windows Installer to Always may prevent some of the newer updates from Windows Update from being applied. Therefore, we recommend that you only set Disable Windows Installer to Always if there is a specific need or an identified threat that you must address.
[User Configuration\Windows Settings\Folder Redirection]
Enable the following settings:
Application Data
Desktop
My Documents
Start Menu
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Explorer]
Enable the following settings:
Remove Map Network Drive and Disconnect Network Drive
Remove Search button from Windows Explorer
Disable Windows Explorer’s default context menu
Hides the Manage item on the Windows Explorer context menu
Hide these specified drives in My Computer (Enable this setting for A through D.)
Prevent access to drives from My Computer (Enable this setting for A through D.)
Hide Hardware Tab
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Task Scheduler]
Enable the following settings:
Prevent Task Run or End
Disable New Task Creation
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Start Menu & Taskbar]
Enable the following settings:
Disable and remove links to Windows Update
Remove common program groups from Start Menu
Disable programs on Settings Menu
Remove Network & Dial-up Connections from Start Menu
Remove Search menu from Start Menu
Remove Help menu from Start Menu
Remove Run menu from Start Menu
Add Logoff to Start Menu
Disable changes to Taskbar and Start Menu Settings
Disable and remove the Shut Down command or Remove and prevent access to the Shut Down command
Note In Windows 2000, this setting is named Disable and remove the Shut Down command. In Windows Server 2003, this setting is named Remove and prevent access to the Shut Down command.
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Desktop]
Enable the following settings:
Hide My Network Places icon on desktop
Prohibit user from changing My Documents path
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Control Panel]
Enable the following setting:
Disable Control Panel
Important When you enable this setting, you prevent administrators from installing any MSI package on to the Terminal Server, even if the explicit Deny is set for the Administrator account.
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System]
Enable the following settings:
Disable the command prompt (Set Disable scripts to No)
Disable registry editing tools
[User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Logon/Logoff]
Enable the following settings:
Disable Task Manager
Disable Lock Computer
For more information about how to lock down Windows Server 2003 Terminal Server Sessions, visit the following Web site:
https://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=7f272fff-9a6e-40c7-b64e-7920e6ae6a0d&DisplayLang=en (https://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=7f272fff-9a6e-40c7-b64e-7920e6ae6a0d&DisplayLang=en)
The Dsacls.exe tool
Dsacls.exe is a command-line tool that you can use to query the security attributes and to change permissions and security attributes of Active Directory objects. It is the command-line equivalent of the Security tab in the Windows Active Directory snap-in tools such as Active Directory Users and Computers and Active Directory Sites and Services. You can use Dsacls.exe to lock out Terminal Services end-users from files and folders on a Windows Server 2003-based computer or a Microsoft Windows 2000-based computer.
For more information about how to use the Dsacls.exe tool (Dsacls.exe) to manage access control lists (ACLs) for directory services in Windows Server 2003 and Microsoft Windows 2000 Server, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
281146 (https://support.microsoft.com/kb/281146/ ) How to use Dsacls.exe in Windows Server 2003 and Windows 2000